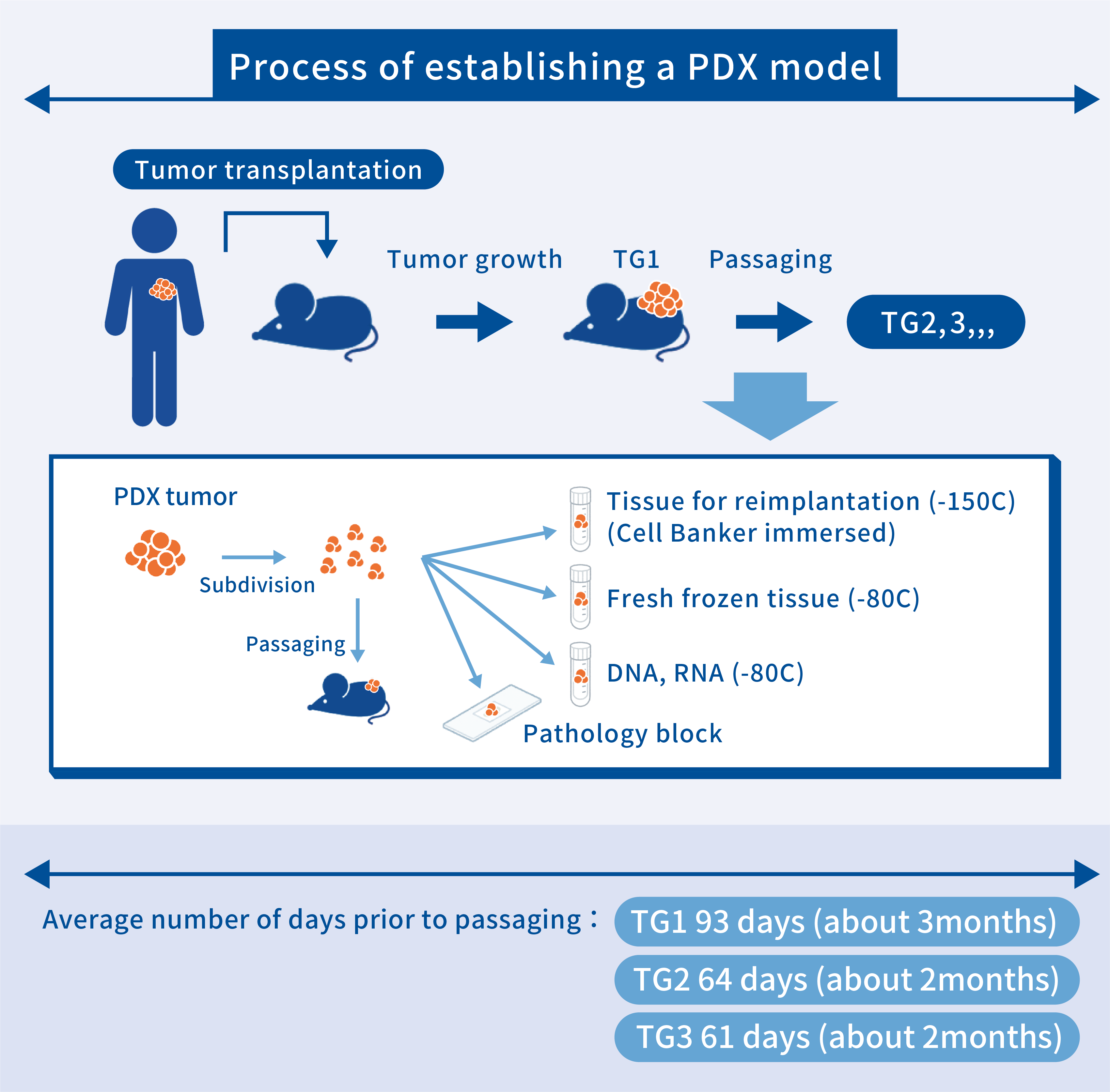
The process of establishing PDX models for inclusion in the J-PDX Library
PDX models in the J-PDX Library have been created using NOG mice, and the engraftment rate is about 30% overall, although there are some differences depending on the type of cancer. The period between transplantation of a patient’s tumor and tumor engraftment in mice tends to be longer than the period between subsequent passaging and engraftment. Completing 3 passages to establish a stable PDX takes an average of 7 months, and sometimes a year or longer is required for slow-growing tumors. During passaging, tissues for reimplantation soaked in an anti-freezing solution for research use, fresh-frozen specimens for nucleic acid and protein analysis, and pathology blocks for pathological analysis are prepared.
*In the J-PDX Library, the mouse in which a patient’s tumor was first transplanted is designated Trans generation 1 (TG1). Successive generations are denoted TG1, TG2, and TG3. Some other institutions supplying PDX models use the terms F0 and F1, but TG1 corresponds to F0.
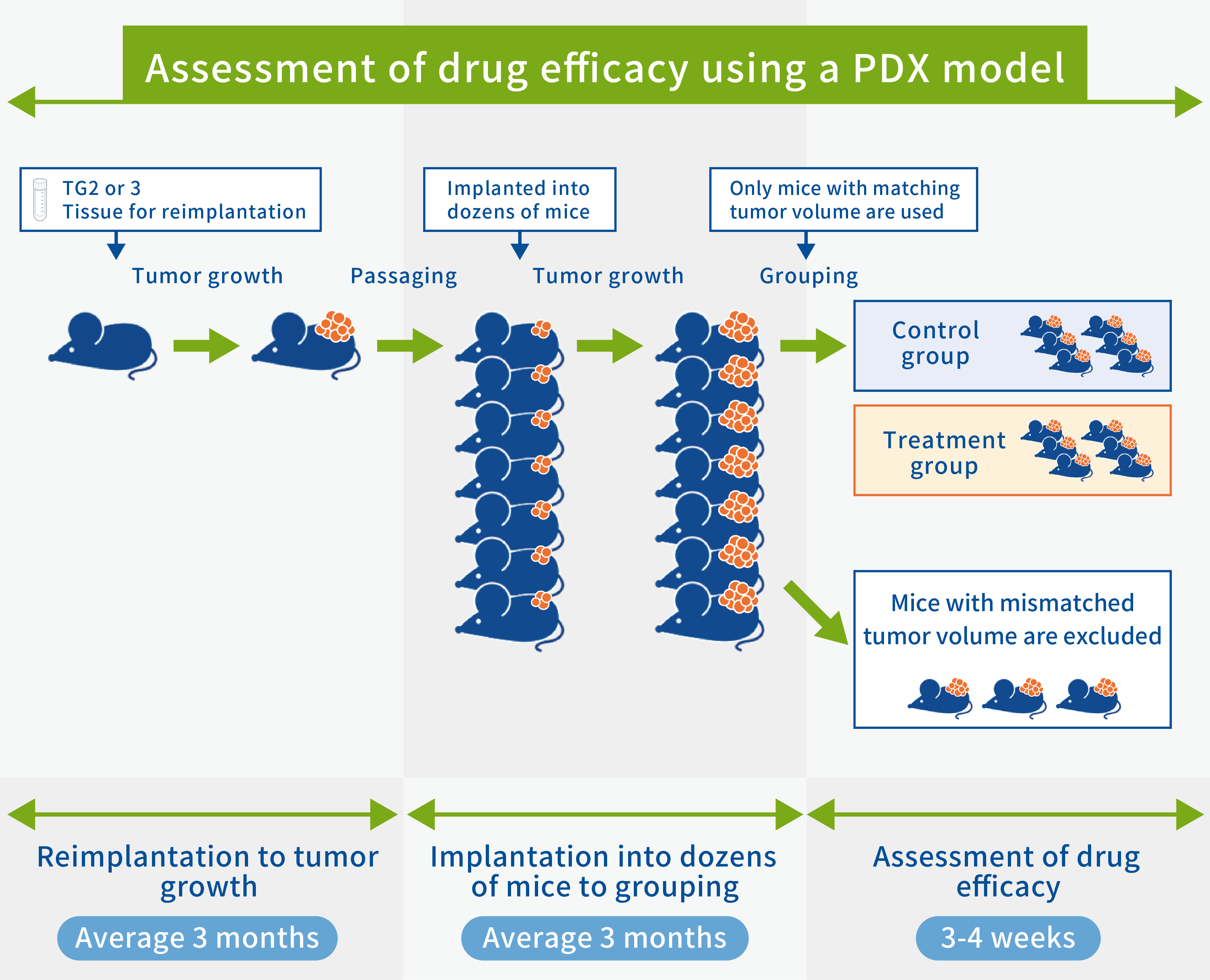
Steps in assessment of drug efficacy using PDX models
When screening anticancer drugs (assessing drug efficacy) using PDX models, the tissues for reimplantation are transplanted back into mice and successively transplanted into multiple mice when they have grown. Tumors in PDX models are highly heterogeneous, so the growth rate of each mouse tumor differs considerably when the tissues are transplanted into multiple mice. This is why we have started experiments by transplanting tissue into 1.5 to 2 times as many mice as are actually required to assess drug efficacy and by completely randomizing the mice depending on the tumor volume at the start of administration. If, for example, we need 6 mice in the control group and 6 in the treatment group (12 mice in total), we transplant tissue into 18 to 24 mice and use 12 mice with the same tumor volume. Mice not used to assess drug efficacy will be used in other experiments or to prepare stored specimens. The steps shown here are a typical use of a PDX, and the method and process of assessment may differ depending on the details of the experiment and PDX used.
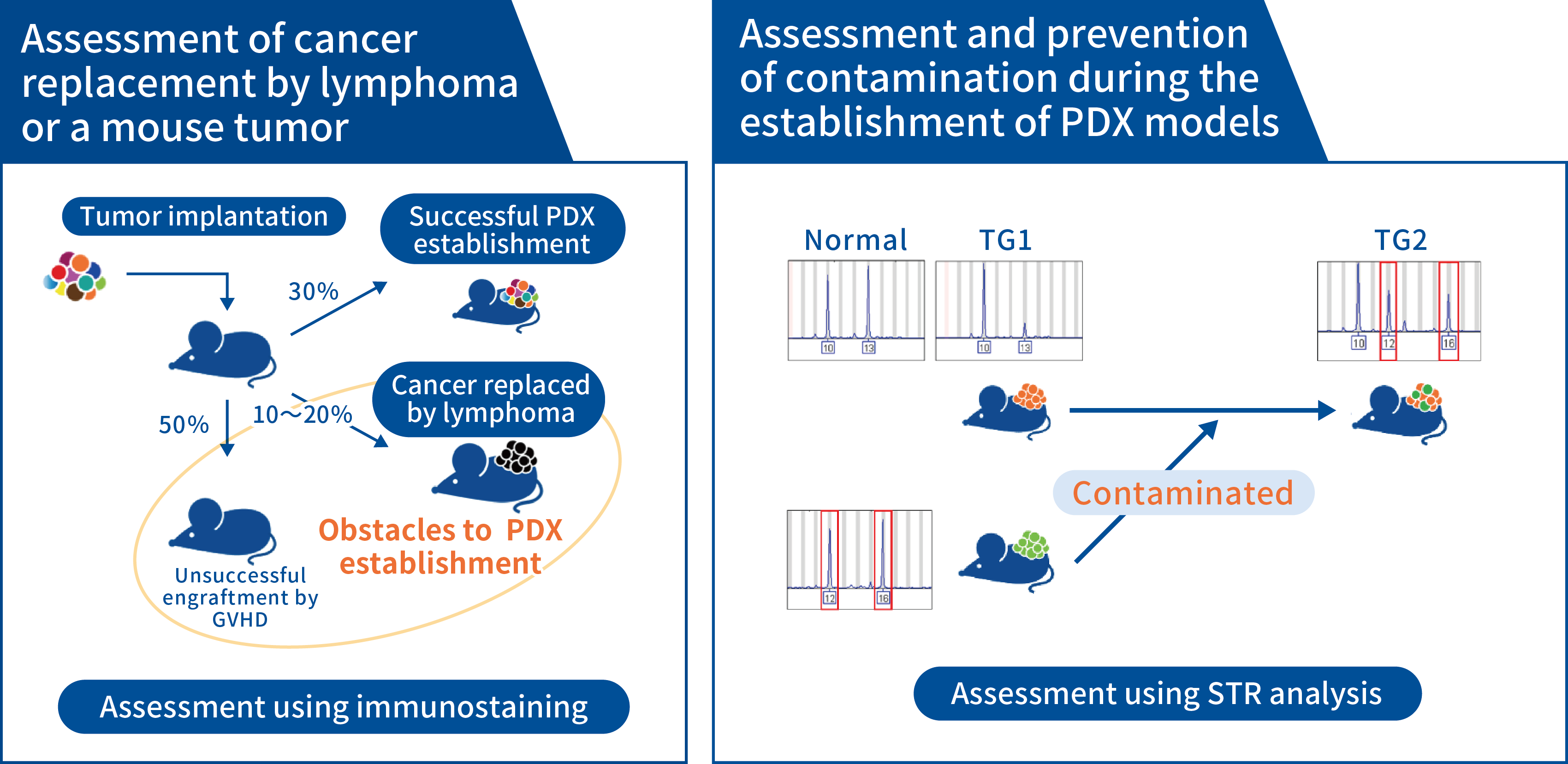
Quality control in the J-PDX Library
In the process of PDX creation, there are instances in which tumors do not grow at all in mice after tumor tissue is transplanted, but there are also instances in which xenograft-associated lymphoproliferative disorders (XALDs) may prevent PDX engraftment. These disorders include “cancer replacement by lymphoma,” in which lymphocytes in the tumor tissue grow to form a tumor, and “graft-versus-host disease (GVHD),” in which lymphocytes attack the host (the mouse). Cancer replacement by a mouse tumor, where a tumor from a mouse grows to replace cancer, is another major factor that inhibits PDX engraftment. In our previous experience with the J-PDX Library, cancer replacement by lymphoma has been observed in about 12% of samples, and especially in samples of gastrointestinal tract tumors such as gastric cancer and colon cancer.
Pathology blocks are prepared during each passage and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), human CD45 antibodies, and human COX-IV antibodies (mitochondria) to exclude cancer replacement by lymphoma or a mouse tumor from the J-PDX Library. Tumors in which cancer has been replaced by lymphoma are positive for human CD45 staining. When cancer has been replaced by a mouse tumor, mitochondrial staining is negative.
Short tandem repeat analysis (STR analysis) is performed to exclude contamination and mix-ups during the process of successive transplantation. Quality control in the J-PDX Library is performed by comparing STRs in PDX tumors to normal DNA and tumor DNA from patients.
Types of samples and information stored in the J-PDX Library
The J-PDX Library stores the following samples and information.
| Classification | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| PDX sample | Tissue for reimplantation | Soaked in an anti-freezing solution and stored at -150°C |
| Fresh frozen tissue | After flash freezing with liquid nitrogen, stored at -80°C | |
| DNA | After extraction, stored at -80°C | |
| RNA | After extraction, stored at -80°C | |
| Pathology block | Embedded in FFPE, Embedded in OCT | |
| Analytical Information | Pathology staining | HE, COXIV, CD45 |
| STR analysis | AmpFLSTR™ Identifiler™ Plus PCR Amplification Kit (ThermoFisher scientific) | |
| Genetic analysis | Panel analysis (Oncomine Comprehensive Assay ver3), whole exon analysis, whole transcriptome analysis, etc. | |
| Growth curve for PDX tumors | ||
| Results of efficacy tests | Partial results only | |
| Clinical information | Age, sex | Partially disclosed while mindful of personal information |
| Method of sample collection, sample collection site | Partially disclosed while mindful of personal information | |
| The type of cancer, histology, primary/recurrent, TNM classification, stage, treatment history, response to treatment, outcome, etc. | Partially disclosed while mindful of personal information |
Information is anonymized to protect personal information and summary data are made publicly available. For more detailed information, refer to the database (J-PDX CATALOG) pursuant to a nondisclosure agreement.
Use of the J-PDX Library
Requests for the use of J-PDX samples
The “Ethics Policy on the Implementation and Use of the J-PDX Library” has been formulated in order to properly manage the samples and information received from patients in the J-PDX Library and to promote the scientific, convenient, and ethically appropriate development and use of PDX models in cancer research. For details, click here.
Samples stored in the J-PDX library are of human origin and require an ethics review and handling based on the “Ethical Guidelines for Life Science and Medical Research Involving Human Subjects.” In addition, the samples and information in the J-PDX Library are “temporary lending” from the National Cancer Center, the Library’s manager, pursuant to an agreement with an external organization and are not “for sale.” Your understanding and cooperation are appreciated.
Procedures for using J-PDX samples
The procedures for using J-PDX samples varies depending on where you are conducting your experiments with them. If you have any questions about the procedures or other questions, please contact us at
ncc_j-pdx_info(at)ml.res.ncc.go.jp.
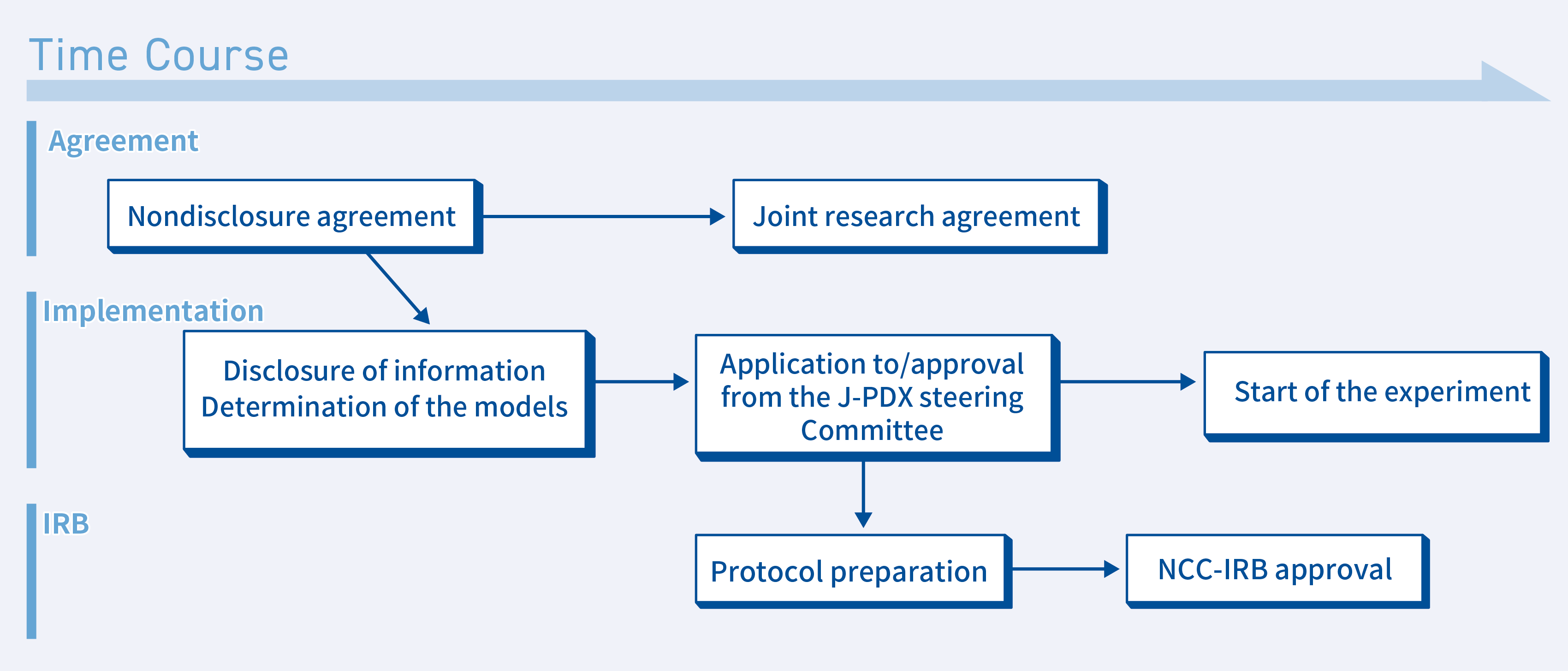
①When conducting an experiment at the NCC in collaboration with the NCC
If you wish to conduct an experiment at the NCC in collaboration with the NCC, the following procedures will be followed.
- Conclusion of a nondisclosure agreement
We also have a sample nondisclosure agreement, so please contact us. - Disclosure of J-PDX-related information and determination of the models that will be used
We will discuss the disclosure of model-related information with you via web conferencing - Application for use submitted to the J-PDX Steering Committee
A PDX can be used once an application for use is submitted to and approved by the NCC. - IRB application
A new IRB application may not be required depending on the nature of the research. A decision will be made based on the nature of the research and how the PDX will be used. - Joint Research Agreements
The NCC and your institution will conclude a joint research agreement. - The experiment starts
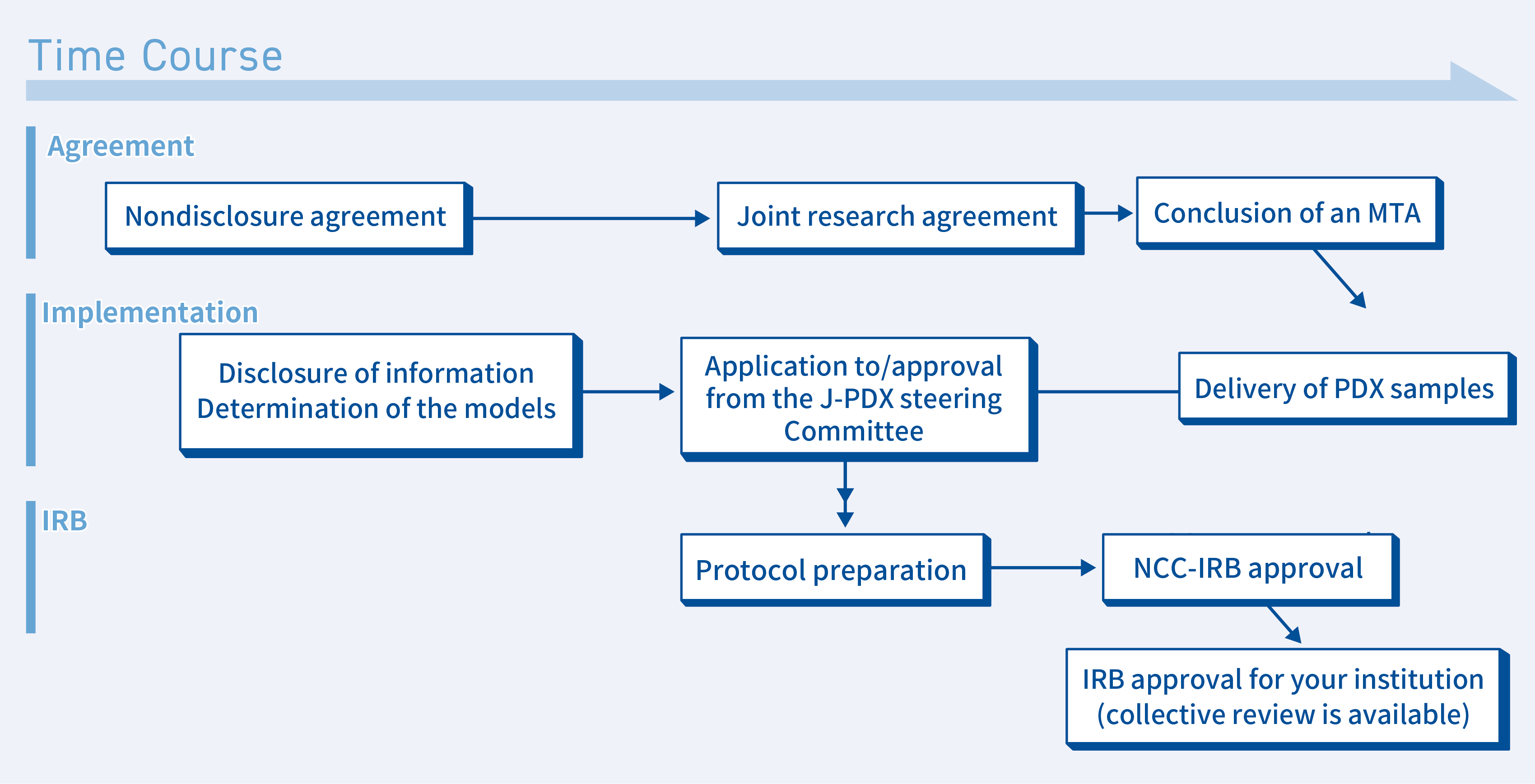
②When an experiment is conducted at your facility in collaboration with the NCC
If you wish to conduct an experiment using a PDX at your facility in collaboration with the NCC, the following procedures will be followed.
- Conclusion of a nondisclosure agreement
We also have a sample nondisclosure agreement, so please contact us. - Disclosure of J-PDX-related information and determination of the models that will be used
We will discuss the disclosure of model-related information with you via web conferencing - Application for use submitted to the J-PDX Steering Committee
A PDX can be used once an application for use is submitted to and approved by the NCC. - IRB application
If you wish to loan samples to an entity other than the NCC, you must obtain approval from the NCC’s Institutional Review Board (IRB). We will jointly prepare a research plan based on the experiment’s details, submit it to the NCC-IRB, and obtain approval. We can also conduct a collective review that includes your institution. - Joint research agreement
The NCC and your institution will conclude a joint research agreement. - Conclusion of an MTA
Once the joint research agreement is concluded and approval is obtained from the IRB, PDX samples will be sent to your institution. At this time, a material transfer agreement (MTA) will be concluded and the samples will be provided to you. - The experiment starts
When an experiment is conducted at your institution, you may be required to obtain approval from your institution’s animal experimentation review board and to submit and obtain approval for the use of genetically modified animals (submission and approval of a protocol for an experiment involving genetic modification) in addition to the procedures above. Please check with your institution to determine what procedures are required.
③When Mediford Corporation is commissioned to conduct an experiment
The PDX models established in the J-PDX library are maintained in parallel by Mediford Corporation in the GLP facility. If you would like to conduct any type of experiment using J-PDX samples via subcontracting, please contact Mediford Corporation (https://www.mediford.com/en/).
Cost of using J-PDX samples
The J-PDX Library is supported by many public funds such as the AMED’s CiCLE project, the National Cancer Center’s Cancer Research and Development Fund, JSPS Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, and joint research funds with commercial organizations. In order to accelerate drug discovery and development with the J-PDX Library and to maintain the Library as an open platform, we ask that researchers who use the J-PDX Library to bear part of the cost of the Library. Please contact us for details.
